Essential Ethical Considerations for Successful AI Adoption: What Every Business Needs to Know

Table of Contents
Introduction
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies has transformed the way businesses operate, enabling efficiencies, enhancing customer experiences, and driving innovation. However, the adoption of AI also raises significant ethical considerations that businesses must navigate carefully. As organizations integrate AI into their operations, they must consider not only the potential benefits but also the ethical implications of their AI strategies. This article delves into the ethical considerations in AI adoption, examines relevant laws guiding AI practices, and explores real-world examples of businesses facing ethical dilemmas in their AI implementations.
Ethical Considerations in AI
1. Transparency and Explainability:
One of the foremost ethical concerns surrounding AI is the need for transparency and explainability. AI systems, particularly those using machine learning algorithms, often operate as “black boxes,” making it challenging for users to understand how decisions are made. Businesses must ensure that AI models are interpretable and that stakeholders can comprehend the reasoning behind AI-generated outcomes.
For example: A notable case is that of IBM Watson- IBM-Watson summary paper , which faced criticism when its healthcare AI system’s technology promised, failed to meet the sky-high expectations set by its marketing team. Not only did it face market deployment issues, it faced significant technical hurdles as it struggled to understand Doctor’s notes (which often contained: abbreviations, medical jargon, etc) despite its ability to understand Natural language which was one of its most celebrated features.
This lack of clarity led to concerns about the trustworthiness of the AI’s suggestions in clinical settings, highlighting the importance of making AI decisions explainable to end-users and improving its processing ability for healthcare settings.
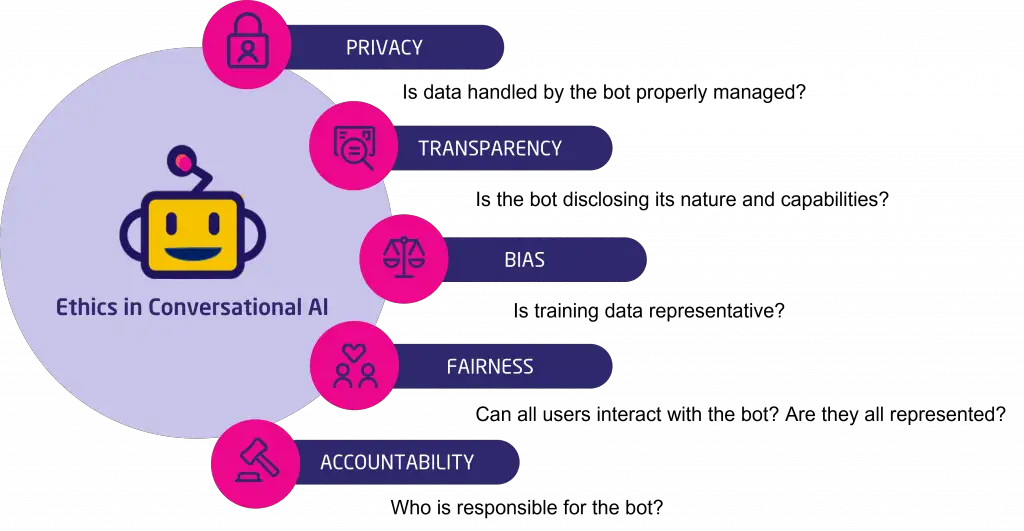
2. Privacy and Data Protection:
AI systems often rely on large datasets, which can include sensitive personal information. Businesses must prioritize privacy and data protection to comply with regulations and maintain customer trust. This involves ensuring that data collection, storage, and processing practices align with ethical standards and legal requirements.
Example: In 2021, Clearview AI faced backlash for scraping images from social media platforms without users’ consent to build its facial recognition database. In 2023, US police used this same database over a million times to identify criminals. These incidents prompted discussions on privacy rights and the ethical implications of using personal data without explicit permission, leading to regulatory scrutiny and lawsuits.
3. Bias and Fairness:
AI systems are only as good as the data they are trained on. If the training data contains biases, the AI can perpetuate or even exacerbate these biases in its decision-making processes. This raises ethical issues of fairness, particularly in sensitive areas like hiring, lending, and law enforcement.
Example: The COMPAS (Correctional Offender Management Profiling for Alternative Sanctions) algorithm, used in the U.S. criminal justice system to assess the likelihood of reoffending, was found to have racial biases. Investigative reports revealed that the algorithm disproportionately flagged Black defendants as higher risk compared to their white counterparts, leading to calls for greater scrutiny and reform in AI applications in criminal justice.

4. Accountability and Responsibility:
When AI systems make decisions, determining accountability can become complex. Businesses need to establish clear lines of responsibility for AI-driven actions, particularly when those actions lead to negative outcomes. Ethical frameworks must be developed to guide decision-making and accountability in AI use.
Example: In 2018, an autonomous vehicle operated by Uber struck and killed a pedestrian in Tempe, Arizona. Investigations revealed gaps in the system’s decision-making processes, raising questions about who was accountable—the company, the software developers, or the vehicle operators. This tragic incident highlighted the urgent need for clear accountability frameworks in AI applications.
Relevant Laws and Regulations
As businesses navigate the ethical landscape of AI adoption, they must also comply with various laws and regulations governing AI use. These laws aim to address ethical concerns related to AI deployment, ensuring accountability, privacy, and fairness.
1. The UNESCO Recommendations on Artificial Intelligence (AI):
This was adopted in November 2021, provide a framework for the ethical development and use of AI globally. A Summary of its Key principles include:
- Human Rights-Centric Approach: AI must respect and protect human rights, including privacy and freedom of expression.
- Inclusivity and Equity: AI systems should promote diversity and avoid marginalizing disadvantaged groups.
- Transparency and Explainability: Stakeholders should understand how AI systems operate- with clear communication about their capabilities and limitations.
- Accountability: Clear lines of responsibility must be established for actions taken by AI technologies.
- Sustainability: AI development should align with sustainable development goals (SDGs).
- International Cooperation: Collaboration among countries and organizations is encouraged to share best practices in responsible AI development.
- Education and Awareness: Public and stakeholder education on AI technologies and ethical considerations is emphasized.
2. AI Ethics Guidelines:
Various organizations and governments have developed AI ethics guidelines to help businesses adopt AI responsibly. For instance, the OECD Principles on Artificial Intelligence emphasize the importance of transparency, accountability, and human-centered values in AI development and implementation. These guidelines serve as a framework for businesses to align their AI strategies with ethical standards.

3. Regulatory Initiatives:
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly focusing on AI. For example, the European Commission has proposed regulations that categorize AI systems based on their risk levels. High-risk AI applications, such as those used in healthcare or law enforcement, would face stricter compliance requirements, reinforcing the need for ethical considerations in AI adoption.
Real-World Case Studies
Case Study 1: Microsoft Recall Saga:
In recent news, Microsoft’s latest Windows 11 feature, Recall, has generated substantial controversy in the tech community. This AI-driven tool aims to enhance user productivity by capturing screenshots of active windows every few seconds, allowing users to easily retrieve past information. However, this seemingly innovative feature has raised significant privacy and security concerns among users and experts alike.
Privacy advocates and security experts are concerned that Recall may unintentionally capture sensitive information, including passwords and personal data. Critics warn that constant screenshot capturing could expose data and increase risks if a device is compromised. This has underscored the necessity for Microsoft to implement stronger privacy controls and transparent data handling practices to alleviate these concerns.
Case Study 2: Google’s Project Maven:
In 2018, Google faced internal and public backlash for its involvement in Project Maven, a U.S. Department of Defense initiative that used AI to analyze drone footage. Employees raised ethical concerns about contributing to military applications, fearing the potential for AI to enhance lethal capabilities.
In response, Google decided not to renew its contract for Project Maven and established AI principles that prohibit the development of AI for use in warfare. This decision reflects the growing importance of ethical considerations in AI partnerships and contracts.
In conclusion as businesses increasingly adopt AI technologies, ethical considerations must be at the forefront of their strategies. Ensuring transparency, fairness, privacy, and accountability are paramount to building trust with stakeholders and mitigating risks associated with AI deployment. Additionally, adherence to relevant laws and regulations is essential for maintaining compliance and fostering responsible AI practices.
References
- Ethics of Artificial Intelligence | UNESCO
- https://www.propublica.org/article/machine-bias-risk-assessments-in-criminal-sentencing
- OECD. (2019). OECD Principles on Artificial Intelligence. Retrieved from OECD – Artificial intelligence | OECD
- The Rise and Fall of IBM Watson: Lessons from AI’s Journey in Healthcare | by Sai kiran Adlluru | Medium
- Justice served? Discrimination in algorithmic risk assessment – Research Outreach
- Self-Driving Uber Car Kills Pedestrian in Arizona, Where Robots Roam – The New York Times
- Microsoft’s Windows 11 Recall: Revolution or Privacy Nightmare?.
- Google to drop Pentagon AI contract after employee objections to the ‘business of war’ – The Washington Post
- Artificial Intelligence – AI | UNESCO