GDP and Startups: Correlations and Opportunities for growth
The GDP of a nation has a correlation to the size and growth of the startups that exist within its ecosystem.
Startups help countries significantly improve their GDP by providing new growth opportunities. Countries with stronger GDPs help their startups find traction fast by providing enabling environments.
GDP in this article is regarded as GDP per capita representing the accurate measure of the prosperity of a nation.
For instance, Nigeria has a GDP of $397.3 billion, while her GDP per capita is $2028.8, compared to South Africa with a GDP of $368.3 billion while her GDP per capita is $6374.03. This disparity is due to the difference in the population that contributes to the GDP. – 2018
Startups have single-handedly driven growth in countries like Israel. Startups are known to rise above economic circumstances in attracting investments having raised from unstable Nigeria to the stable United states and defying the risk involved to achieve phenomenal results. Startups are known to withstand economic recessions, meltdowns and pandemics to stay in business and grow. These proven possibilities present an avenue for startups to contribute immensely to the economy – Thereby increasing the GDP.
Startups may be new companies and start relatively small compared to other conglomerates. Still, they do play a significant role in economic growth. They create new jobs which mean more employment, and the increase in employment improves the economy.
Startups contribute to economic diversity. They incite innovation and encourage competition. New entrepreneurs can bring new ideas needed to stir innovation and generate competition to the table.
Startups are different from small businesses as they have an extensive direct impact on the cities in which they are headquartered. Microsoft changed Redmond and Google transformed Mountain View, California, Infosys changed Bangalore, Alibaba transformed Hangzhou. These companies started relatively small and grew, to alter the cities where they operated, providing job opportunities to both experienced and young professionals.
NIGERIA
“Nigeria is the premier investment destination on the African continent in 2018.”
Disrupt Africa Funding Report
Nigeria has a large population of about 200 million people. However, the crippled purchasing power of the population has made the addressable market for several niches of the economy to be considerably lower than the people. This low purchasing power has, in many ways, impeded the growth of startups in Nigeria.
In Nigeria, Startups are constrained by the basics of a typical business environment. Power outages, poor access to finance, political instability and corruption pose severe constraints on startup growth in Nigeria.
Despite these odds, Nigeria has the largest startup ecosystem in Africa, with more than 500 active and viable startups. Nigeria is fast becoming a hub for startups with cities like Lagos, Abuja, Ibadan, Kano and Aba at the forefront of this movement.
Nigeria’s e-commerce leader Jumia employs about 3,000 workers, and 100,000 more workers who help customers place orders (Adegoke, 2018). Similarly, Uber, which launched in Nigeria in 2013, has created 7,000 jobs in the country (Ubabukoh, 2017).
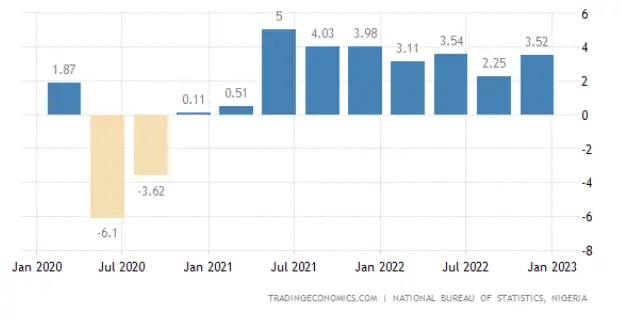
How GDP growth defies projection:
The Israel case study
Israel has the highest density of startups in the world; With a population of around 8.5 million and about 4000 startups, it has the largest number of startups per capita in the world, with around one startup per 1,400 people.
After the United States, Israel has more companies listed on the NASDAQ than any other country in the world, including India, China, Korea, Singapore, and Ireland,
Israel’s economy has also grown faster than the average for the developed economies of the world in most years since 1995. Even the wars Israel has repeatedly fought failed to stop it from achieving this feat.
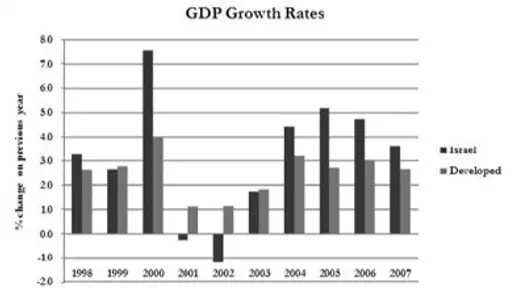
During the six years following 2000, Israel was hit not just by the bursting of the global tech bubble but by the most intense period of terrorist attacks in its history and by the second Lebanon war.
Yet Israel’s share of the global venture capital market did not drop—it doubled, from 15 per cent to 31 per cent. And the Tel Aviv stock exchange was higher on the last day of the Lebanon war than on the first, as it was after the three-week military operation in the Gaza Strip in 2009. The sheer enabling environment for startups results in a healthy economy that is not moved by the noise of war.
How startups help the economy and contribute to the GDP
Startups are engines of growth. Methods must be sought to foster competition and assist transformational entrepreneurs in order to avoid economic stagnation,
Eric Corl
Startups are engines of growth. Methods must be sought to foster competition and assist transformational entrepreneurs in order to avoid economic stagnation,
- Creates opportunities by opening up new markets
E-commerce was almost non-existent before Amazon stole the show. Today, it is a whole non-negligible sector of economies worth trillions of dollars. Amazon is an example out of many.
- Increase employment
Older companies seem to create more jobs. However, when we consider the concept of net job creation, it would become evident that they are mostly job destroyers. Older companies tend to lay off workers as they try to adopt less cumbersome processes to improve their efficiency.
Startups on the bright side are new; hence all the jobs they create are unique and are a net positive with regard to job creation.
According to Business Dynamics Statistics, a U.S. government dataset compiled by the U.S. Census Bureau, between 1977 and 2005, existing companies lost a total of 1 million jobs per year. in comparison, startups added an average of 3 million jobs. – Startups, in this study, are defined as firms younger than one-year-old.
- Transform their immediate surrounding
Startups attract fresh talent to areas they find themselves in and in no time transform the cities, bringing in wealth and a truckload of job opportunities through value created.
- Improve technology
Startups invest in new technologies and cutting-edge innovation as opposed to trying to improve older technologies and incremental innovation.
This disruptive approach to technology by startups most times yields impressive results. These startups are often results acquired by much bigger companies (Google, Microsoft) that can use their economy of scale to push innovation further.
How GDP affects startups
- Ability to innovate
In developing countries(countries with lower GDP per capita), bureaucratic barriers and costs are the main setbacks for startups and their ability to invariably their ability to innovate.
- Cost of doing business
Ömer Doruk and Ergül Söylemezoğlu investigated the startup procedures, and startup cost effect on new business establishment relations in 61 developing countries. Startup costs and startup procedures are some of the main impediments to innovation.
- Tendency to stay in business.
In countries with high GDP per capita, the business environment is usually more conducive. Startups find it easier to set up shop, and secure funding to focus on innovation and development of the cutting-edge technologies that help them run successful businesses. This increases their tendency to stay in business considerably.
In conclusion,
Startups are affected by the policy, credibility and stability of their immediate country as this is the first basis of interaction with the rest of the world. Governments must take measures that help these infant wonders, that add immense value to the economy, to walk unscathed through their formative years.






3 Comments
Comments are closed.